Learning ELMo
ELMo: Embeddings from Language Models
一、ELMo介绍
参考:
Paper:Deep contextualized word representations
ELMo section of the AllenNLP website
1 ELMo简介
我们介绍了一种新型的深层语境化单词表示,它建模了(1)单词使用的复杂特征(例如,语法和语义),以及(2)这些用法在不同的语言环境中是如何变化的(例如,建模一词多义)。我们的词向量是深度双向语言模型(biLM)内部状态的习得函数,该模型是在大型文本语料库上预先训练的。
2 ELMo特点
- Contextual:每个单词的表示取决于它所使用的整个上下文。
—— 单词表示不再使用固定的词向量,解决了一词多义的问题
- Deep:单词表示结合了深度预训练神经网络的所有层。
—— ELMO模型的不同层能够学习到不同级别的信息,较高层能够捕获和上下文相关的词义信息(适合词义消歧任务),较低层能够捕获语法方面的信息(适合词性标注任务)。因此,应用到下游任务时,不仅仅使用网络最后一层的输出,而是将不同层的表示进行线性组合,让下游任务选择最合适的表示。
- Character based:单词表示是纯粹基于字符的,允许网络通过形态学特征对训练中未出现的词汇表外的token形成一个健壮的表示。
—— 在ELMO模型输入部分,一个词的embedding由构成词的字母序列的embeddings做卷积池化得到,能够一定程度上学习到单词的形态学特征,解决OOV问题。
3 预训练任务
双向的语言模型(biLM):
(1)前向语言模型
-
以给定上文,计算下一个词的概率的方式计算文本对应token序列的概率。即: \(p\left(t_{1}, t_{2}, \ldots, t_{N}\right)=\prod_{k=1}^{N} p\left(t_{k} | t_{1}, t_{2}, \ldots, t_{k-1}\right)\)
-
对应任务:给定上文$(t_1,…,t_{k-1})$,预测下一个词$t_k$。
(2)后向语言模型:给定下文$(t_{k+1},…,t_n)$,预测上一个词$t_k$。
-
以给定下文,计算上一个词的概率的方式计算文本对应token序列的概率。即: \(p\left(t_{1}, t_{2}, \ldots, t_{N}\right)=\prod_{k=1}^{N} p\left(t_{k} | t_{k+1}, t_{k+2}, \ldots, t_{N}\right)\)
-
对应任务:给定下文$(t_{k+1},…,t_N)$,预测上一个词$t_k$。
训练目标:
最大化前向和后向语言模型的对数似然,即:
\[\begin{array}{l}{\sum_{k=1}^{N}\left(\log p\left(t_{k} | t_{1}, \ldots, t_{k-1} ; \Theta_{x}, \vec{\Theta}_{L S T M}, \Theta_{s}\right)\right.} \\ {\left.\quad+\log p\left(t_{k} | t_{k+1}, \ldots, t_{N} ; \Theta_{x}, \overleftarrow{\Theta}_{L S T M}, \Theta_{s}\right)\right)}\end{array}\]其中, $\Theta_{x}$ 为模型token表示层的参数, $\Theta_{s}$为模型 Softmax层的参数,$\vec {\Theta}{LSTM}$ 为前向LSTM的参数, $\overleftarrow {\Theta}{LSTM}$ 为后向LSTM的参数。
4 模型结构
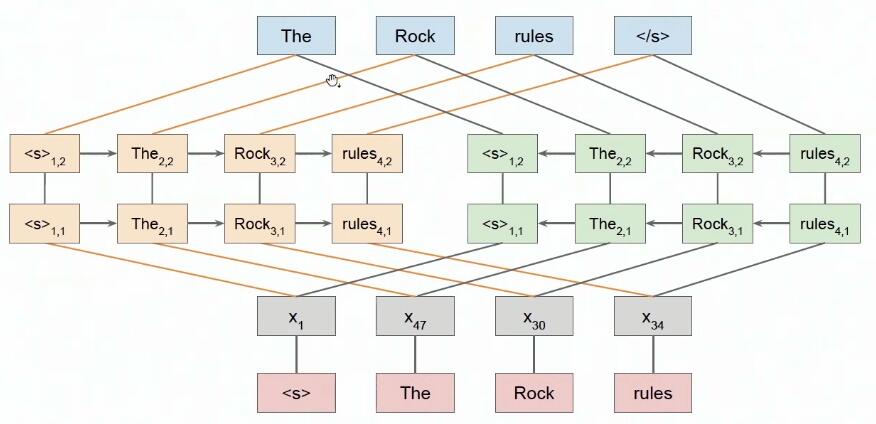
Elmo的双向语言模型是用双向的多层LSTM实现的(上图以两层为例)。
注意:
- 这不是多层的bi-LSTM,也不能用此结构替代。(这将导致标签泄漏的问题)
- 上图中,前向的语言模型,从下往上看;后向的语言模型,应从上往下看(和前向比输入输出要换过来,并逆置)。
- 上图省略了char卷积(模型输入部分得到word-embedding的结构),highway network(位于char卷积后面),不同lstm层之间的残差连接。
5 Elmo应用到下游任务
-
一个拥有L层biLM 的Elmo结构,对于每一个token $t_k$,有$2L+1$个表示。
\[\begin{aligned} R_{k} &=\left\{\mathrm{x}_{k}^{L M}, \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{k, j}^{L M}, \overleftarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{k, j}^{L M} | j=1, \ldots, L\right\} \\ &=\left\{\mathbf{h}_{k, j}^{L M} | j=0, \ldots, L\right\} \end{aligned}\]$其中$,
$x_{k}^{LM}$是token $t_k$基于char卷积得到的word-emdedding;$\overrightarrow {h}{k,j}^{LM}$为token $t_k$在第$j$层前向$LSTM$中的隐状态,$\overleftarrow {h}{k, }^{LM}$为token $t_k$在第$j$层后向$LSTM$中的隐状态。
除了$h_{k,0}^{LM}=\left[x_{k}^{LM};x_{k}^{LM}\right]$,$h_{k,j}^{LM}=\left[\overrightarrow {h}{k,j}^{LM}, \overleftarrow{h}{k,j}^{LM}\right]$ 是token $t_k$ 在第 $j$ 层两个方向LSTM中隐状态的拼接。
-
对于下游任务,如何应用token $t_k$的$2L+1$个表示$R_k$:
-
最简单的做法
只取ELMo两个方向lstm的最高层表示,并拼接,即:$ELMo_{k}=E\left(R_{k}\right)=h_{k, L}^{L N}$
-
更普遍的做法
根据特定任务task,对不同层的”两个方向的表示的拼接“进行加权平均,即: \(\mathbf{E L M o}_{k}^{\text {task}}=E\left(R_{k} ; \Theta^{\text {task}}\right)=\gamma^{\text {task}} \sum_{j=0}^{L} s_{j}^{\operatorname{tas} k} \mathbf{h}_{k, j}^{L M}\) $其中,S^{task}是各层的权重,\gamma^{t a s k}是一个 scalar型参数,用于调整 ELMo向量的大小。$
$ELMo只提供表示\mathbf{h}_{k, j}^{L M},S^{task}和\gamma^{t a s k}都是需要下游任务自己去学习的$
-
二、ELMo实践
pip install allennlp,allennlp下有两种方法,获取预训练的ELMo表示。
1 方法1
通过allennlp.modules.elmo模块调用。API doc
通过该模块能够将ELMo应用到自己的模型中,并且能够自动学习ELMo各层表示对应的权重。
示例:
from allennlp.modules.elmo import Elmo, batch_to_ids
options_file = "https://allennlp.s3.amazonaws.com/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_options.json"
weight_file = "https://allennlp.s3.amazonaws.com/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_weights.hdf5"
# Compute two different representation for each token.
# Each representation is a linear weighted combination for the 3 layers in ELMo (i.e., charcnn, the outputs of the two BiLSTM))
elmo = Elmo(options_file, weight_file, 2, dropout=0)
# use batch_to_ids to convert sentences to character ids
sentences = [['First', 'sentence', '.'], ['Another', '.']]
character_ids = batch_to_ids(sentences)
embeddings = elmo(character_ids)
# embeddings = {'elmo_representations': elmo_representations, 'mask': mask}
# embeddings['elmo_representations'] is length two list of tensors.
# Each element contains one layer of ELMo representations with shape (2, 3, 1024).
-
Class Elmo的初始化参数
def __init__(self, options_file: str, weight_file: str, num_output_representations: int, requires_grad: bool = False, do_layer_norm: bool = False, dropout: float = 0.5, vocab_to_cache: List[str] = None, keep_sentence_boundaries: bool = False, scalar_mix_parameters: List[float] = None, module: torch.nn.Module = None) # options_file : ``str``, required. ELMo JSON options file # weight_file : ``str``, required. ELMo hdf5 weight file # num_output_representations: ``int``, required. The number of ELMo representation to output with different linear weighted combination of the 3 layers (i.e.,character-convnet output, 1st lstm output, 2nd lstm output). # 根据下游任务需要几个表示取值,一般的任务对每个token仅仅需要一个表示,即取值为1。不同的表示,仅仅是加权求和的权重不同。 # requires_grad: ``bool``, optional. If True, compute gradient of ELMo parameters for fine tuning. #如果为True,为fine tuning模式,ELMo的参数也将被更新。默认为False,即用feature-based的方式应用到下游任务。
2 方法2
通过allennlp.commands.elmo.ElmoEmbedder模块调用,该方式不会学习各层表示的权重。API doc
示例:
from allennlp.commands.elmo import ElmoEmbedder
options_file = "https://allennlp.s3.amazonaws.com/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_options.json"
weight_file = "https://allennlp.s3.amazonaws.com/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_weights.hdf5"
sentences = [['First', 'sentence', '.'], ['Another', '.']]
elmo = ElmoEmbedder(options_file=options_file, weight_file=weight_file, cuda_device=0)
elmo_embedding, elmo_mask = elmo.batch_to_embeddings(sentences)