文本分类二
1.深度学习方法做文本分类
- 使用深度学习方法进行文本分类时,可以使用word2vec,glove,fasttext等工具预训练词向量,或者直接使用开源的训练好的词向量。
- 深度学习方法一般都是基于CNN、RNN以及Attention机制对文本进行特征提取,表示成文本向量,最后接一个softmax层进行分类。
2.利用RNN、Attention机制进行文本分类
(1)TextRNN
本质上是对seq2seq Translation模型Encoder部分的应用。
-
表示:
-
直接取encoder最后一个时刻的输出$h_n$,作为文本的向量表示。
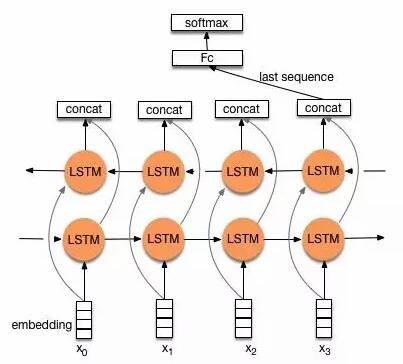
-
将encoder各个时刻的输出加和取平均,作为文本的向量表示。
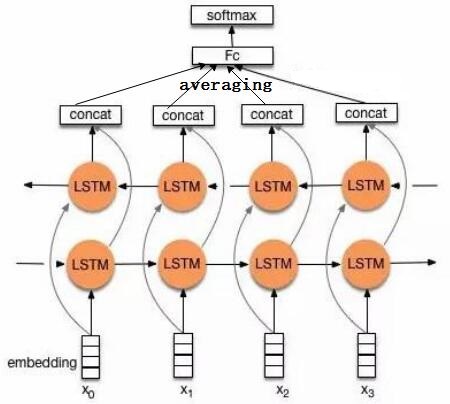
note:
一般选用LSTM、GRU比裸的RNN要好一点,还可以指定单向/双向,单层/多层等。
-
-
分类
根据多分类还是二分类问题,输出层选用softmax或者sigmoid。
(2)TextRNN+Attention机制
本质是对上文TextRNN的第二种文本表示方式的该进。
-
表示
-
思路
文本的向量表示不再取encoder各个时刻的输出的平均,而是认为不同单词对文本主题的反应程度不同,给每个时刻的输出乘以一个权重,故文本表示为encoder各个时刻的输出的加权平均。
-
模型结构
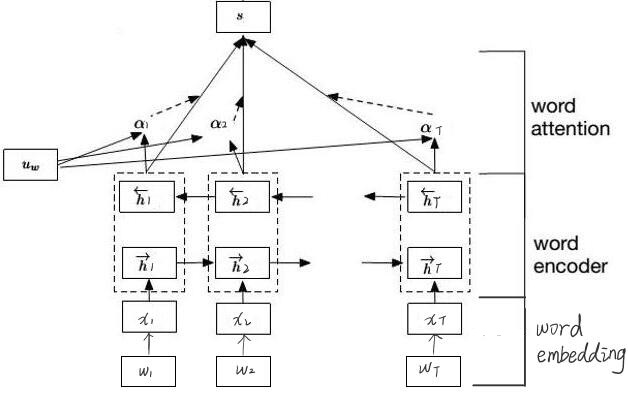
-
word embedding
- 词向量表$W_e$可以使用Word2vec等工具预训练的词向量,也可以先随机初始化一个词向量表,然后词向量随模型一起训练。
- 对于单词$w_t$,其词嵌入$x_{t}$如下
-
word encoder
- 双向gru编码
句子中的每个单词就是gru中的一个时刻,先查询词向量表, 得到单词对应的词向量,然后将词向量喂 给这个gru,然后可以得到一个正向的输出和一个反向的输出,接着把正向和反向的输出向量串接起来,作为当前时刻的输出。
\[\vec{h_{t}}=\vec{gru}(x_t),t\in[1,T] \\ \overleftarrow {h_t}=\overleftarrow{gru}(x_t),t\in[1,T]\\ h_t=[\vec{h_{t}},\overleftarrow {h_t}]\] -
Word Attention
因为文本中每个单词对文本主题的重要性不相同,因此使用Attention机制描述每个单词的重要性。对word encoder中每个单词的输出$h_t$乘以一个权重$\alpha_t$ ,再求和作为文本的向量表示$s$。
\[u_t=tanh(W_w h_t+b_w)\\ \alpha_t=\frac{exp(u_{t}^Tu_w)}{\sum_t exp(u_{t}^Tu_w)}\\ s=\sum_t \alpha_t h_t\]- $tanh(W_w h_t+b_w)$相当于一个线性层
- $\alpha_t=\frac{exp(u_{t}^Tu_w)}{\sum_t exp(u_{t}^Tu_w)}$其实是一个点乘+一个softmax层
- $u_w$是一个和模型一起训练的向量参数
- note:这里使用的权重计算方式,只是Attention求权重的众多方式之一
-
分类
先经过一个线性层将文本表示v映射到类别数目,再根据问题用softmax或者sigmoid输出各个类别的概率。 \(p=Softmax(W_cs+b_c)\)
-
-
(3)HAN
分层注意网络(Hierarchical Attention Network)
-
简述:
在TextRNN+Attention的基础上考虑文本句间的关系。
-
要点
- 不再把整个文本当成一个句子。而是根据句子是由单词组成,文档由句子组成的原则,先使用单词的词向量表示句子,再此基础上以句子向量构建文档的信息表示。
- 句子中的单词对句子的贡献也有差异,每一个句子对文本的重要性也有所不同。在句子表示和文本表示时均引入Attention机制计算权重,用加权平均代替单一的平均。
-
网络结构
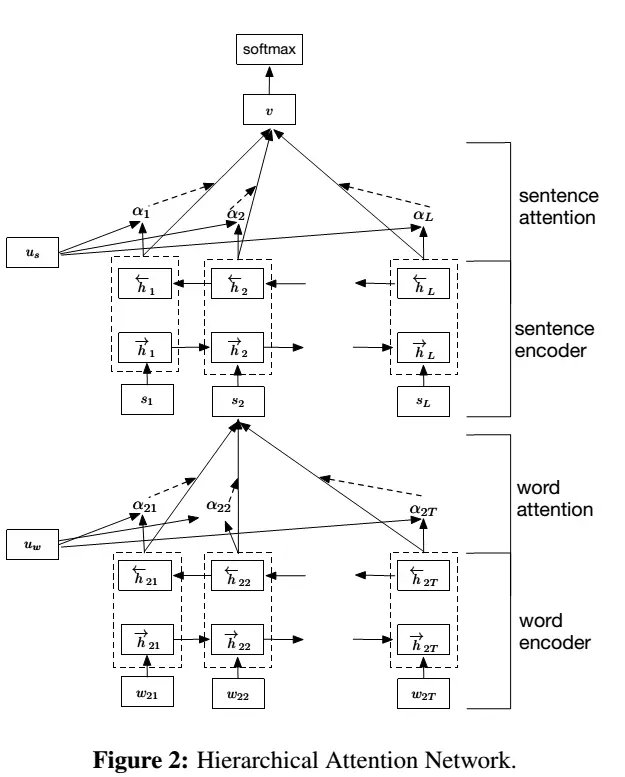
- 结构解析
-
word embedding
- 词向量表$W_e$可以使用$Word2Vec$等工具预训练的词向量,也可以先随机初始化一个词向量表,然后词向量随模型一起训练。
- 对于第$i$个句子的第$t$个单词$w_{it}$,其词嵌入$x_{it}$如下
-
word encoder
- 双向gru编码
对于一个句子中的每个单词就是gru中的一个时刻,先查询词向量表$W_e$, 得到单词对应的词向量$x_{it}$,然后将词向量喂 给这个gru,然后可以得到一个正向的输出和一个反向的输出,接着把正向和反向的输出向量串接起来,作为当前时刻的输出。
\[\vec{h_{it}}=\vec{gru}(x_{it}),t\in[1,T] \\ \overleftarrow {h_{it}}=\overleftarrow{gru}(x_{it}),t\in[1,T]\\ h_{it}=[\vec{h_{it}},\overleftarrow {h_{it}}]\] -
Word Attention
因为句子中每个单词对句子的重要性不相同,因此使用Attention机制描述每个单词的重要性。对一个句子每个单词在word encoder层的输出$h_{it}$乘以一个权重$\alpha_{it}$ ,再求和作为句子的向量表示$s_i$。
\[u_{it}=tanh(W_w h_{it}+b_w)\\ \alpha_{it}=\frac{exp(u_{it}^Tu_w)}{\sum_t exp(u_{it}^Tu_w)}\\ s_i=\sum_t \alpha_{it} h_{it}\] -
Sentence Encoder
类同word encoder,只不过把词向量换成了句子向量。
-
通过前面的word encoder和word attention的方法,我们可以得到一 个文本中所有句子的向量表示。
-
这里我们仍然用一个双向的gru,然后把每个句子作为一个时刻,按顺 序将句子向量喂到gru里面。同样地,我们会得到一个正向和一个反向的输 出,我们再把这两个输出拼接到一起,作为当前时刻的输出。
-
-
Sentence Attention
类同Word Encoder,只不过把词向量换成了句子向量,求的是句子之间的权重。
同样考虑不同句子对分类的重要程度不同,对各个句子的输出$h_i$做加权平均得到整个文本的向量表示$v$。 \(u_i=tanh(W_s h_i+b_s)\\ \alpha_i=\frac{exp(u_{i}^Tu_s)}{\sum_i exp(u_{i}^Tu_s)}\\ v=\sum_i \alpha_i h_i\)
-
分类
先接一个线性层将文本表示v映射到类别数目,再根据问题用softmax或者sigmoid输出各个类别的概率。 \(p=Softmax(W_cv+b_c)\)
-
-
网络搭建
class Word_attn(nn.Module): def __init__(self, lang_size, hidden_size, pretrained_weight, class_num): super(Word_attn, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.class_num = class_num self.embedding = nn.Embedding(lang_size, hidden_size) # print(pretrained_weight.size()) self.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_weight) self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, bidirectional=True) self.h_linear = nn.Linear(2*self.hidden_size, 2*self.hidden_size) self.a_linear = nn.Linear(2*self.hidden_size, 1, bias=False) self.output = nn.Linear(2*hidden_size, self.class_num) self.soft_max = nn.Softmax() def forward(self, input, hidden0): embedded = self.embedding(input) # [batch, seq] --> [batch, seq, feature] input = embedded.permute(1, 0, 2) #[seq, batch, feature] outputs, hidden = self.gru(input, hidden0) #[seq, batch, 2*hidden_size], [2, batch, hidden_size] x = outputs.permute(1, 0, 2) x = self.h_linear(x) #[batch, seq, 1, 2*hidden_size] x = self.a_linear(x) #[batch, seq, 1] x = self.soft_max(x) attn_weight = x.permute(0, 2, 1) #[batch,1,seq] sent_wv = torch.bmm(attn_weight, outputs.permute(1, 0, 2)) #[batch,1,seq] * [batch, seq, 2*hidden_size] == [batch, 1, 2*hidden_size] # output_class = self.output(sent_wv) #[batch, 1, class_num] return sent_wv def initHidden(self, batch_size): result = Variable(torch.zeros(2, batch_size, self.hidden_size)) #训练集并不正好按batch_size划分 if use_cuda: return result.cuda() else: return result class Sen_attn(nn.Module): def __init__(self, sen_max_length, hidden_size, class_num): super(Sen_attn, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.class_num = class_num self.gru = nn.GRU(2*self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size, bidirectional=True) self.h_linear = nn.Linear(2*self.hidden_size, 2*self.hidden_size) self.a_linear = nn.Linear(2*self.hidden_size, 1) self.output = nn.Linear(2*hidden_size, self.class_num) self.soft_max = nn.Softmax() def forward(self, input, hidden0): #input [seq, batch, feature] outputs, hidden = self.gru(input, hidden0) #[seq, batch, 2*hidden_size], [2, batch, hidden_size] x = outputs.permute(1, 0, 2) x = self.h_linear(x) #[batch, seq, 1, 2*hidden_size] x = self.a_linear(x) #[batch, seq, 1] x = self.soft_max(x) attn_weight = x.permute(0, 2, 1) sent_wv = torch.bmm(attn_weight, outputs.permute(1, 0, 2)) sent_wv = sent_wv.squeeze(1) # [batch, 2*hidden_size] output_class = self.output(sent_wv) #[batch, class_num] return output_class def initHidden(self, batch_size): result = Variable(torch.zeros(2, batch_size, self.hidden_size)) if use_cuda: return result.cuda() else: return result
参考链接
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~diyiy/docs/naacl16.pdf
https://www.jianshu.com/p/37422ce8b2d7